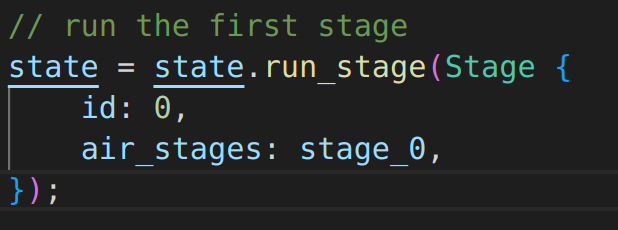
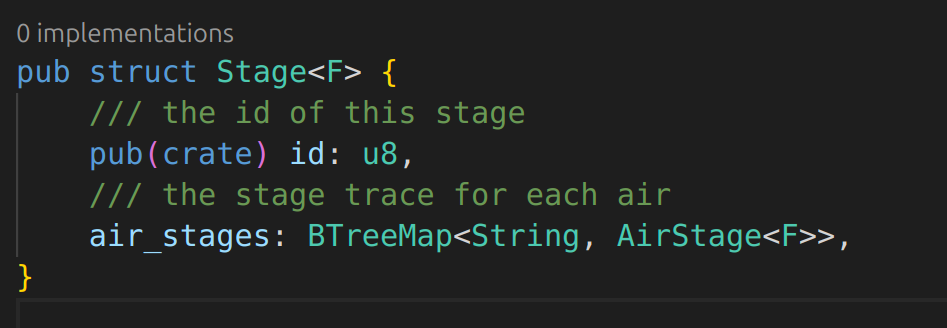
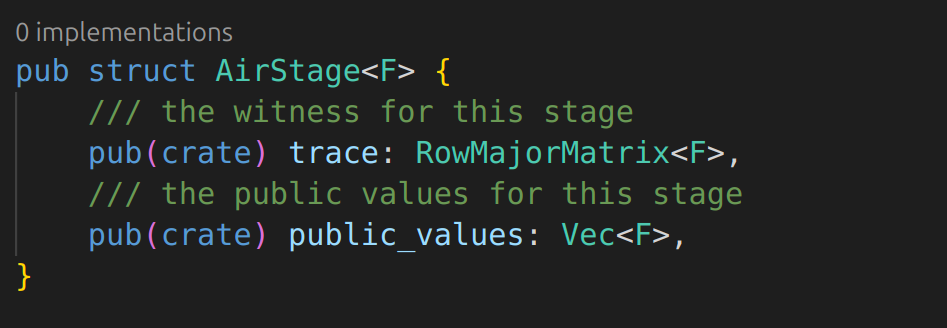
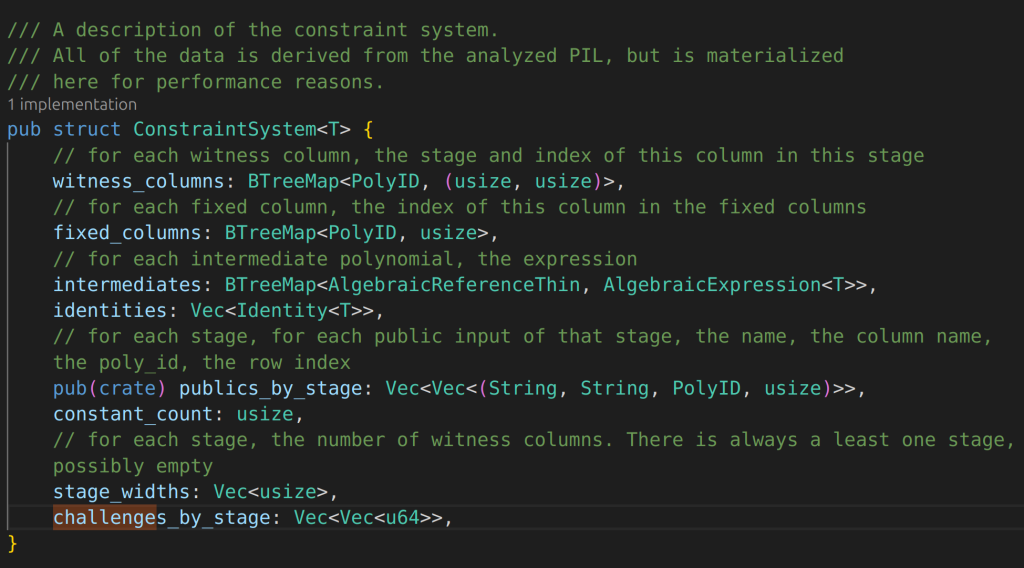
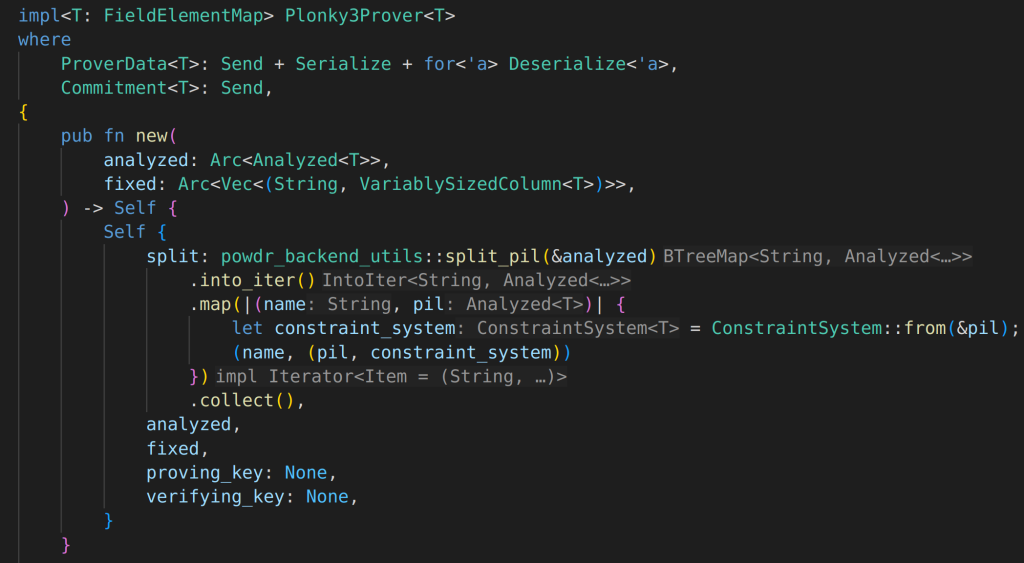
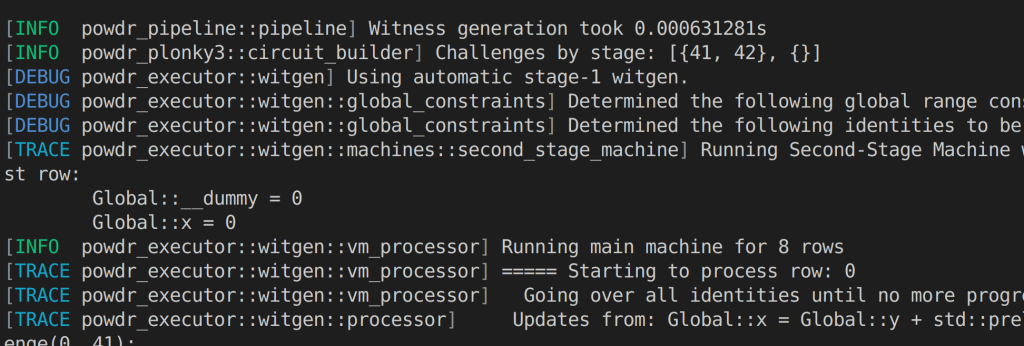
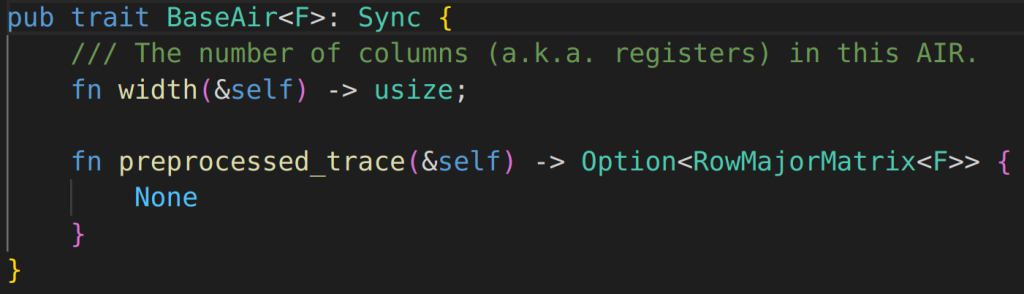
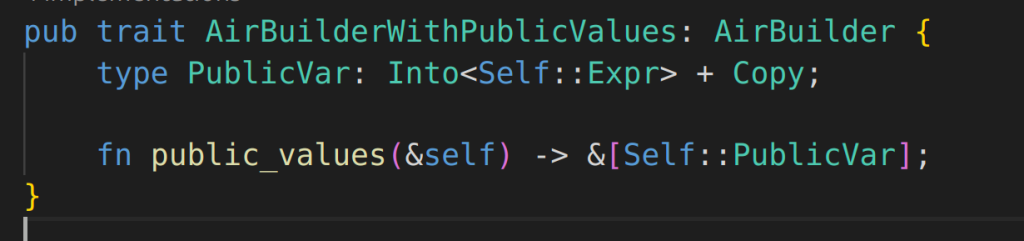
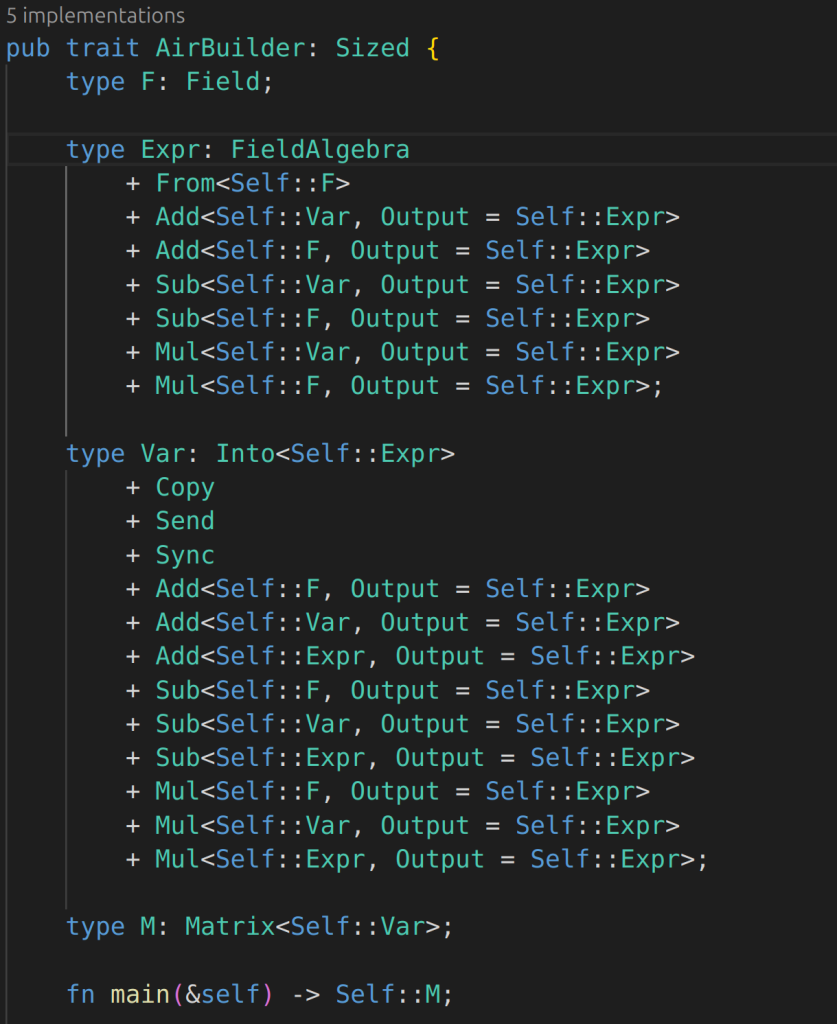
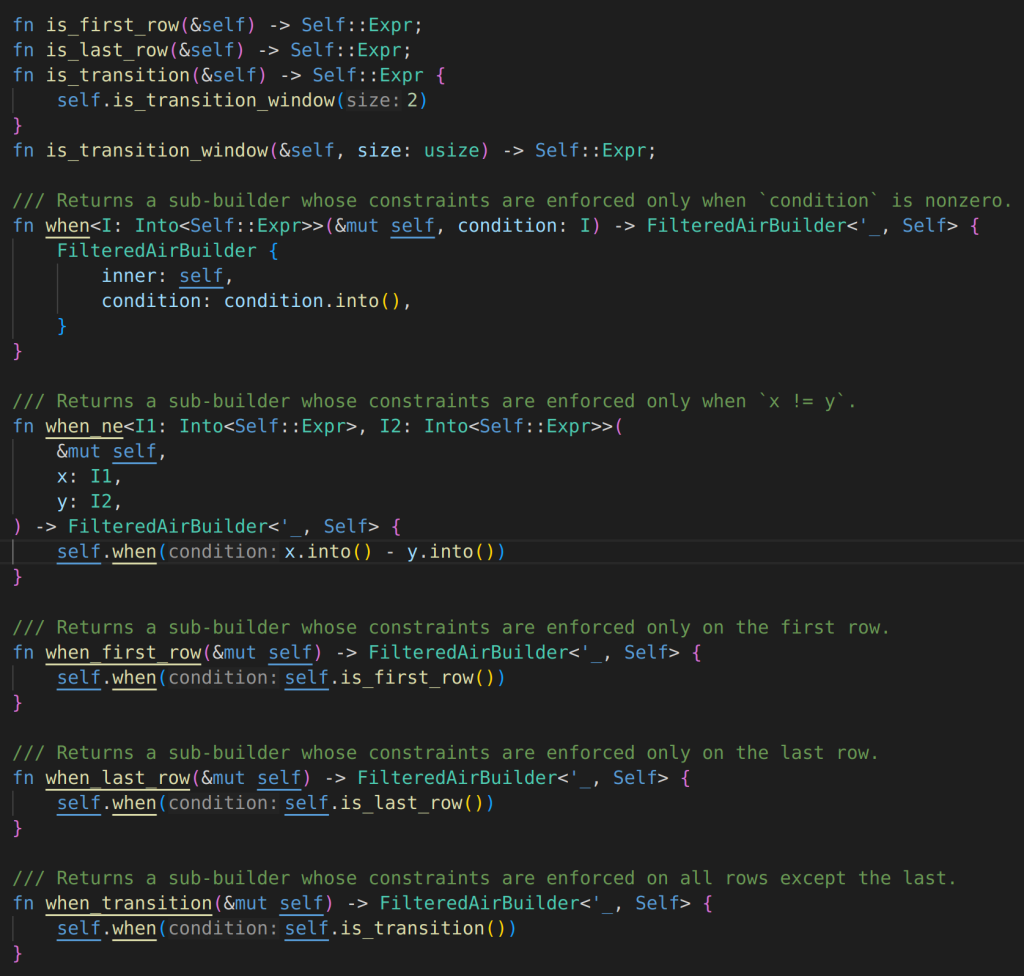
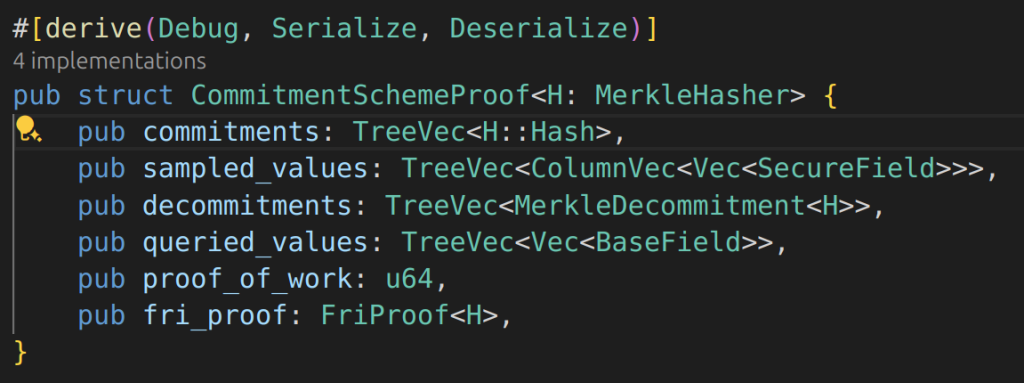
Trying to understand from this PR
understanding lookup.asm

let is_first: col = |i| if i == 0 { 1 } else { 0 };the above line, defines fix column, fix columns are columns known during circuit setup, independent of the what the witness will be. “i” represent the row …